The DigitalOcean Spaces modules enable you to monitor, list or create buckets and files in your DigitalOcean Spaces account.
Prerequisites
-
A DigitalOcean Spaces account
In order to use DigitalOcean Spaces with Boost.space Integrator, it is necessary to have a DigitalOcean Spaces account. If you do not have one, you can create a DigitalOcean Spaces account at DigitalOcean website.
![[Note]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/note.png) |
Note |
|---|---|
|
The module dialog fields that are displayed in bold (in the Boost.space Integrator scenario, not in this documentation article) are mandatory! |
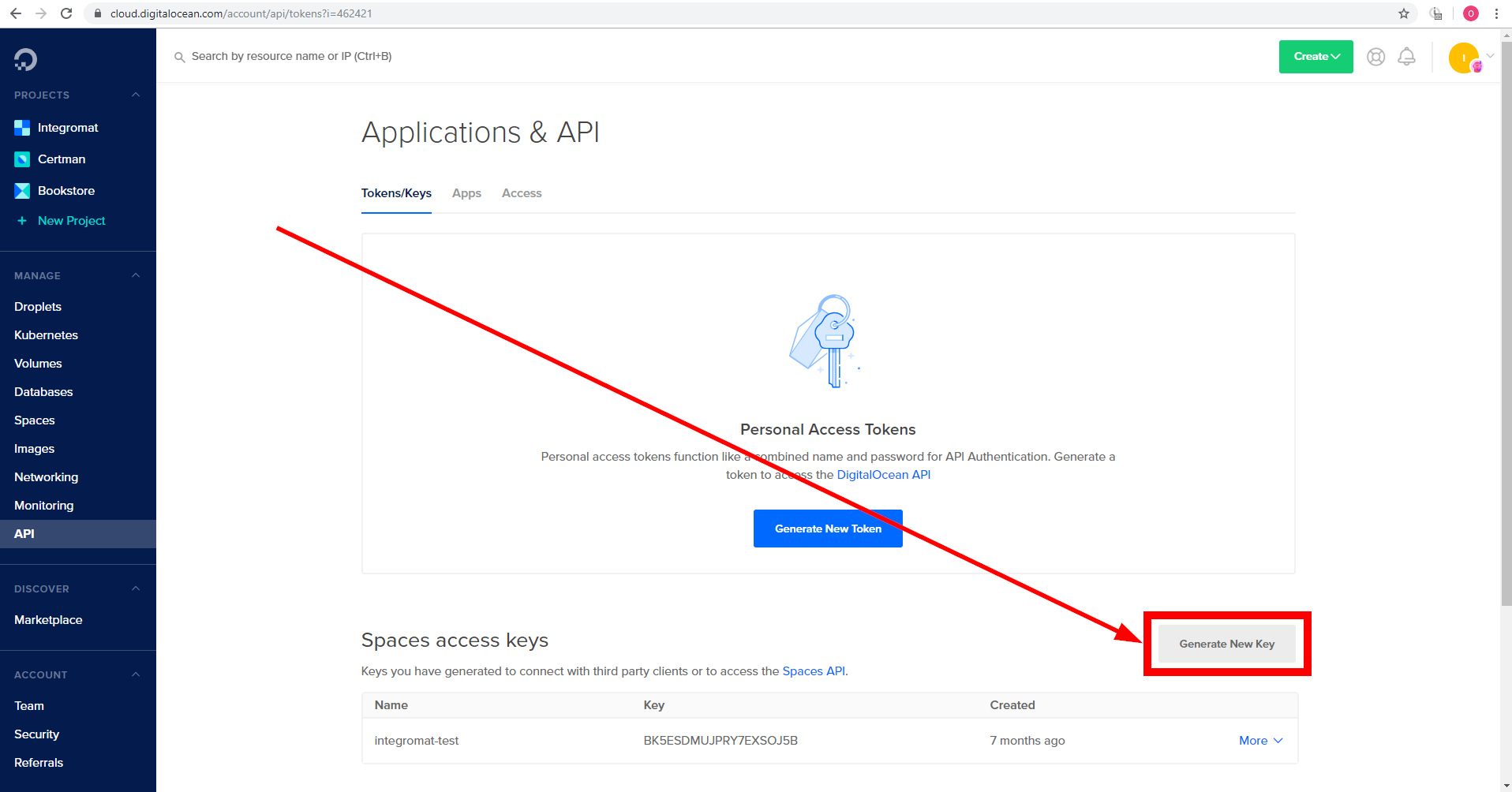
To connect your DigitalOcean Spaces account to Boost.space Integrator you need to obtain the Access Key and Access Secret Key.
-
Log in to your DigitalOcean account.
-
Open the Manage > API section from the menu on the left.
-
Scroll down to the Spaces access keys section and click the grey Generate New Key button.
-
Enter the name for the new access key and press Enter.
-
Copy the provided Access Key and Access Secret Key.
-
Go to Boost.space Integrator and open the DigitalOcean Spaces module’s Create a connection dialog.
-
Enter the Access Key and Access Secret Key you have copied in step 5 to the respective fields and click the Continue button to establish the connection.
Returns the bucket’s name and creation date when the bucket is created in your account.
|
Connection |
|
|
Region |
Select the region you want to retrieve buckets from. |
|
Limit |
Set the maximum number of buckets Boost.space Integrator will return during one execution cycle. |
Retrieves all buckets in your account.
|
Connection |
|
|
Region |
Select the region you want to retrieve buckets from. |
|
Limit |
Set the maximum number of buckets Boost.space Integrator will return during one execution cycle. |
Creates a new bucket in the specified region.
|
Connection |
|
|
Name |
Enter the name for the new bucket. |
|
Region |
Select the region you want to create a new bucket at. |
Returns the file’s name, size, and date modified when the file is uploaded or updated in the bucket.
|
Connection |
|
|
Region |
Select the region that contains the bucket you want to watch for files. |
|
Bucket |
Select the bucket you want to watch for new or updated files. |
|
Prefix |
Enter the path you want to watch files at. |
|
Limit |
Set the maximum number of files Boost.space Integrator will return during one execution cycle. |
Retrieves all files in the specified bucket.
|
Connection |
|
|
Region |
Select the region that contains the bucket you want to list files from. |
|
Bucket |
Select the bucket you want to list the files from. |
|
Prefix |
Enter the path you want to list files from. E.g. |
|
Limit |
Set the maximum number of files Boost.space Integrator will return during one execution cycle. |
Downloads a file from the specified bucket.
|
Connection |
|
|
Region |
Select the region that contains the bucket you want to download the file from. |
|
Bucket |
Select the bucket you want to download the file from. |
|
Path |
Enter the path to the file you want to download E.g. |
Uploads a file to a bucket.
|
Connection |
|
|
Region |
Select the region that contains the bucket where you want to upload a file. |
|
Bucket |
Select the bucket you where you want to upload a file. |
|
Folder |
Enter the path of the target location. Leave empty to upload the file to the root of the bucket E.g. |
|
Source File |
Map the file you want to upload from the previous module (e.g. HTTP > Get a File or Dropbox > Get a file), or enter the file name and file data manually. |
|
Headers |
Insert headers if needed. See common headers or additional headers that can be used here. |
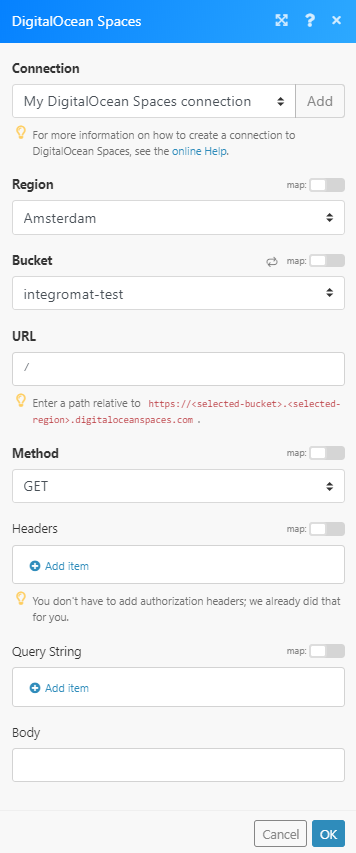
Allows you to perform a custom API call.
|
Connection |
||||
|
URL |
Enter a path relative to
|
|||
|
Method |
Select the HTTP method you want to use: GET to retrieve information for an entry. POST to create a new entry. PUT to update/replace an existing entry. PATCH to make a partial entry update. DELETE to delete an entry. |
|||
|
Headers |
Enter the desired request headers. You don’t have to add authorization headers; we already did that for you. |
|||
|
Query String |
Enter the request query string. |
|||
|
Body |
Enter the body content for your API call. |