An arrayWithin a bundle, data items of the same type are sometimes in an array. You can find an array by looking at the details of a bundle. Depending on the details of your scenario, you can map other modules to a specific item in an array or use iterators and aggregators to manipulate your data into other formats. When mapping,... is a special type of itemItems are rows in records (order/request/invoice/purchase...). A simple array contains one or more text values. A complex array contains one or more collections of the same type. An example of a complex array is the email attachment. The Watch emails modulea module is an application or tool designed to handle specific business functions, such as CRM, project management, or inventory. The system's modular architecture allows you to activate only the modules you need, enabling customization and scalability as your business requirements evolve. returns an array of attachments for every email. Every attachment represents a collection that may contain a name, content, size, etc.
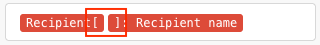
If you map the array’s Recipient name item, it will appear in the field like this:
The number between the square brackets is an index that determines which element of the array will be used. Leaving it empty defaults to the first element.
MappingMapping links the modules in your scenario. When you map an item, you connected the data retrieved by one module to another module to perform the desired action. For example, you can map the email address and subject lines from the Email > Watch emails module to Google Sheets > Add a row and create a spreadsheet of email addresses... an array’s nth element
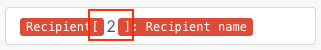
If you wish to access another element, enter or map a value between the square brackets. In the below example, enter 2 to select the second element.
Some arrays contain several collections with key and value itemsItems are rows in records (order/request/invoice/purchase...). These are typically various metadata, attributes, etc.
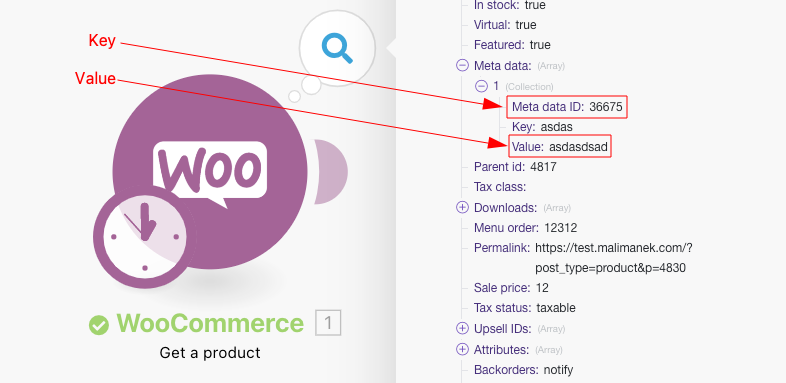
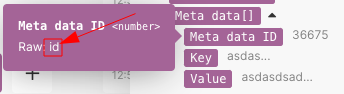
The following example shows the output of the WooCommerce > Get a product module that contains the item Meta data, which is an array of collections. Each collection contains the key item Meta Data ID and the value item Value:
The typical requirement is to lookup an element by its given key value and to obtain the corresponding value from the value item. This can be achieved with a formula employing a combination of themap ()andget ()functionsFunctions you can use in Boost.space Integrator - create, update, delete, get, search..
The following example shows how to obtain the value of the Value item of the element with key Meta data ID item value equal to 20642
 |
The result of the formula will be “no”.
The detailed breakdown of the formula follows:
- The 1st parameter of the
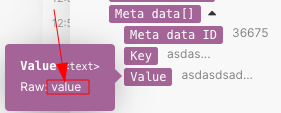
map()functionFunctions you can use in Boost.space Integrator - create, update, delete, get, search. is the whole array item. - The 2nd parameter is the raw name of the value item. To obtain the raw name, hover the mouse cursor over the item in the mapping panel:
![[Important]](https://docs.boost.space/wp-content/themes/bsdocs/docs-parser/HTML/css/image/important.png)
Important All parameters are case sensitive. Even though in this particular example the item’s labelIn Boost.space, a label is a tag that can be added to items within a module. It's a flexible tool used to categorize and organize data, making it easier to customize workflows and processes. differs from its raw name only in capitalization, it is necessary to use the raw name, which is all lowercase valuein contrast to the labelValue - The 3rd parameter is the raw name of the key item:
- The 4th parameter is the given key value.
Because the map() function returns an array (as there could be more elements with the given key value), it is necessary to apply the get() function to get its first element:
- The 1st parameter of the
get()function is the result of themap()function. - The 2nd parameter is the element’s index – one.
See also our Extract an item and/or its value from an array of collections video tutorial.
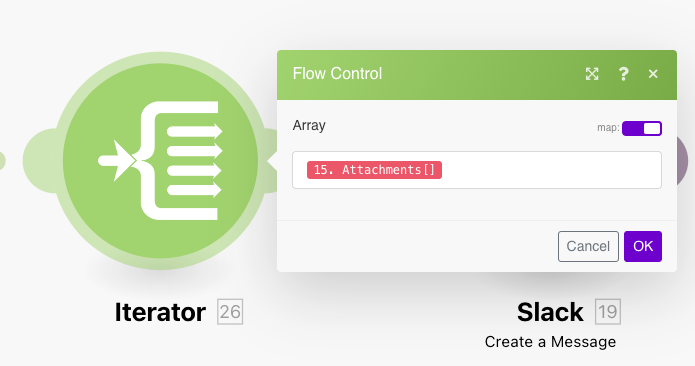
Arrays can be converted to a series of bundles using the Iterator module:
| Important | |
|---|---|
| The outputs from modulesa module is an application or tool designed to handle specific business functions, such as CRM, project management, or inventory. The system's modular architecture allows you to activate only the modules you need, enabling customization and scalability as your business requirements evolve. wrapped between an IteratorWhen creating a scenario, use an iterator to divide one bundle into smaller separate bundles. Subsequent modules then process the bundles separately. One common use is when automatically uploading email attachments to a cloud drive. You can find iterators under the Flow control of the tools section. and AggregatorYou can use a table aggregator to create a table from multiple bundles. The table aggregator merges values based on your specified column and row parameters and outputs into a single bundle. One possible use is compiling blog posts or emails into a single email summary. are not accessible beyond the AggregatorAn aggregator is a type of module that allows you to merge multiple bundles into one single bundle. Aggregators are useful in making data readable for certain modules or generating meaningful output. Boost.space Integrator offers: <br> Array aggregator<br> Numerical aggregator<br> Table aggregator<br> Text aggregator<br> module. |