Common MCP Clients
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open protocol that enables clients such as code editors, browsers, and other developer tools to send structured, real-time context to AI models and copilots. MCP improves the usefulness and accuracy of AI assistants by supplying them with relevant information such as file trees, userCan use the system on a limited basis based on the rights assigned by the admin. selections, metadata, and more.
This article provides an overview of commonly used MCP-compatible clients and how they interact with the protocol.
1. Cursor
Cursor is an AI-native code editor that deeply integrates with MCP to send rich development context to its built-in assistant.
- Documentation: Cursor docs – MCP
- Features:
- Shares file structure, code selections, open tabs, and more with the AI.
- Offers inline and chat-based assistant capabilities.
2. Visual Studio Code (VS Code)
VS Code, through its Copilot Chat extensions, supports acting as an MCP client to share context with AI agents such as GitHub Copilot or custom AI services.
- Documentation: VS Code Copilot Chat → MCP
- Features:
- Shares the current workspace, active files, and user interactions.
- Allows integration with external MCP servers.
3. Windsurf
Windsurf is an AI-native browser interface and development platform that acts as an MCP client by design.
- Documentation: Windsurf Docs → MCP
- Features:
- Sends structured browser and app context to the AI assistant.
- Tailored for research workflows, allowing intelligent AI interaction across browser sessions.
4. Anthropic Claude
Anthropic’s Claude allows usersCan use the system on a limited basis based on the rights assigned by the admin. to create AI apps and chains with powerful context management. It supports MCP-compatible integrations for enhanced contextual understanding.
- Documentation: Anthropic Docs → MCP
- Features:
- Accepts structured MCP context from clients like Cursor, VS Code, or custom appsCreate your own custom apps to be used in the integrator engine and share them with users in your organization..
- Provides tools to debug and test context-sharing.
Step-by-step guide
Before we dive into the individual steps, you’ll need the following:
1. Claude Desktop app (Pro plan or higher).
2. MCP TokenA secure code used to authenticate and authorize access to API endpoints, enabling users to connect with third-party applications. – A secure MCP token you generate in your Boost.spaceA platform that centralizes and synchronizes company data from internal and external sources, offering a suite of modules and addons for project management, CRM, data visualization, and more. Has many features to optimize your workflow! instance to authenticate the communication.
3. URL – A dedicated connectionUnique, active service acces point to a network. There are different types of connections (API key, Oauth…). URL, which you’ll find in the MCP Token section after creating the token
You’ll find out how to get your MCP token and URL in the step-by-step guide below.
Steps to connect Boost.space MCP
1. Open Claude Desktop.
2. In the top menu bar, click Developer → Open App Config File.
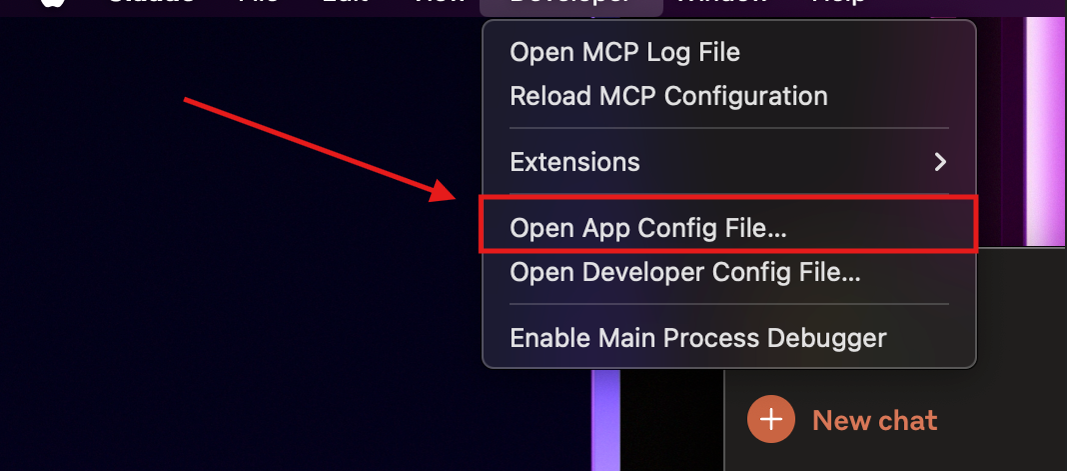
- This opens the
claude_desktop_config.jsonfile where MCP servers are configured.
3. Paste the MCP server block
{
"mcpServers": {
"boostspace": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"mcp-remote",
"YOUR_DEDICATED_MCP_URL",
"--header",
"Authorization: Bearer YOUR_MCP_TOKEN"
]
}
}
}
- Replace
YOUR_DEDICATED_MCP_URLwith the exact Boost.space MCP URL. - Replace
YOUR_MCP_TOKENwith your token from Boost.space
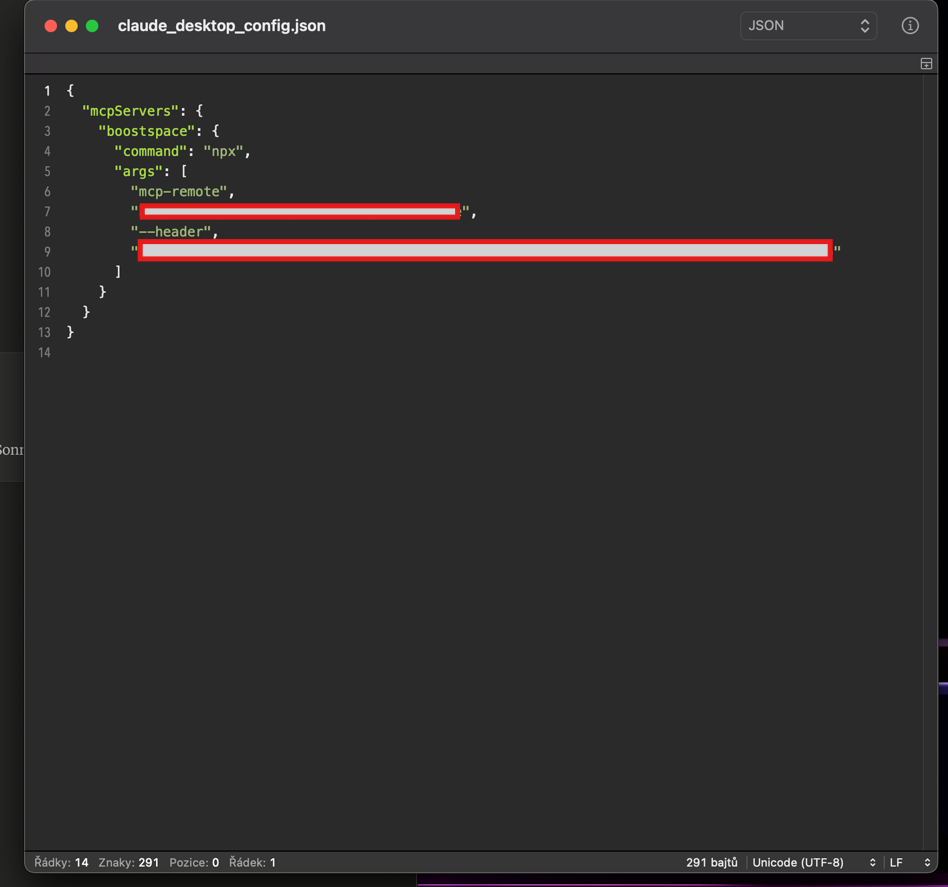
4. Save and restart Claude Desktop
- Save the JSON file.
- Quit and restart Claude Desktop so the new config loads.
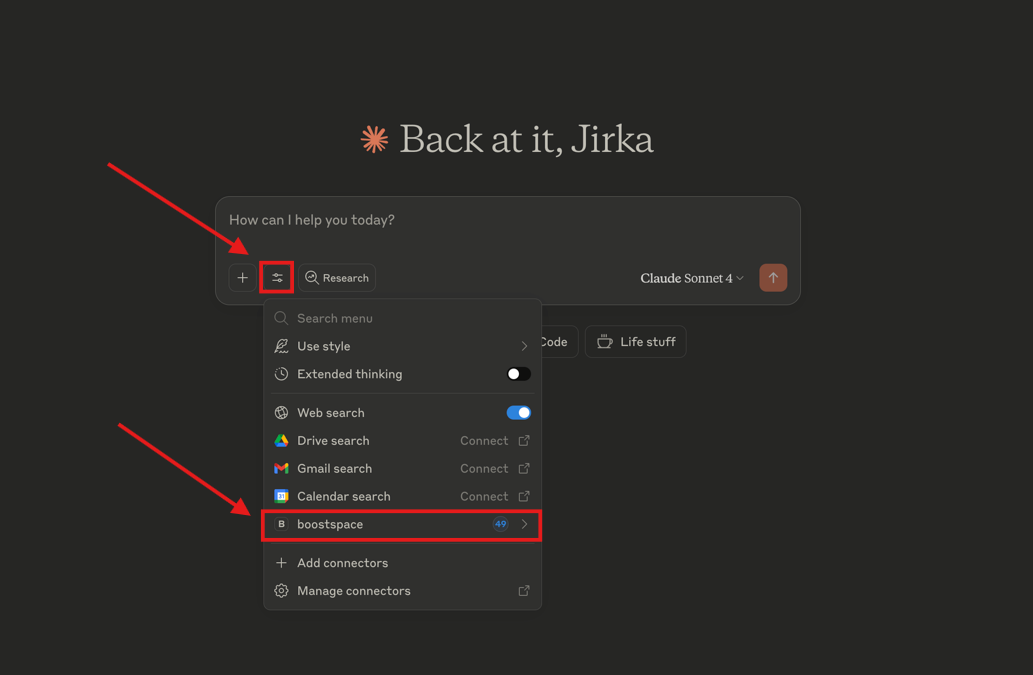
5. Verify the connection
- Open Claude again.
- In the chat window, click on the two stacked lines icon in the chat window.
- You should see Boost.space MCP listed and ready to use.
5. OpenAI (ChatGPT)
ChatGPT by OpenAI supports MCP-based context ingestion via its Custom GPTs or assistant APIs. You can build a bridge that delivers contextual data (like documents, selections, or files) from your app to ChatGPT using an MCP-compatible server.
- Step-by-step integration guide: How to Connect a Remote MCP Server to OpenAI
- Usage:
- Set up a remote MCP server that communicates with OpenAI’s APIs.
- Common use cases include integrating file systems, chat histories, CRM data, or user sessions into the AI prompt.