Uploading files into Boost.space modules
This article provides a structured approach to uploading files into Boost.spaceA platform that centralizes and synchronizes company data from internal and external sources, offering a suite of modules and addons for project management, CRM, data visualization, and more. Has many features to optimize your workflow! modulesa module is an application or tool designed to handle specific business functions, such as CRM, project management, or inventory. The system's modular architecture allows you to activate only the modules you need, enabling customization and scalability as your business requirements evolve.. The process is applicable across various use cases, whether the objective is to attach a product image, store a document within a custom recordIn Boost.space, a record is a single data entry within a module, like a row in a database. For example, a contact in the Contacts module or a task in the Tasks module., or integrate files into any other modulea module is an application or tool designed to handle specific business functions, such as CRM, project management, or inventory. The system's modular architecture allows you to activate only the modules you need, enabling customization and scalability as your business requirements evolve. that supports file fields.
The procedure consists of three main stages: retrieving the file from an external source, preparing it in the appropriate format, and transmitting it to Boost.space via its API. We begin by obtaining the file using a suitable module — for example, through an HTTP request to download it from a specified URL, or by sourcing it from cloud storage platforms such as Google Drive or Dropbox.
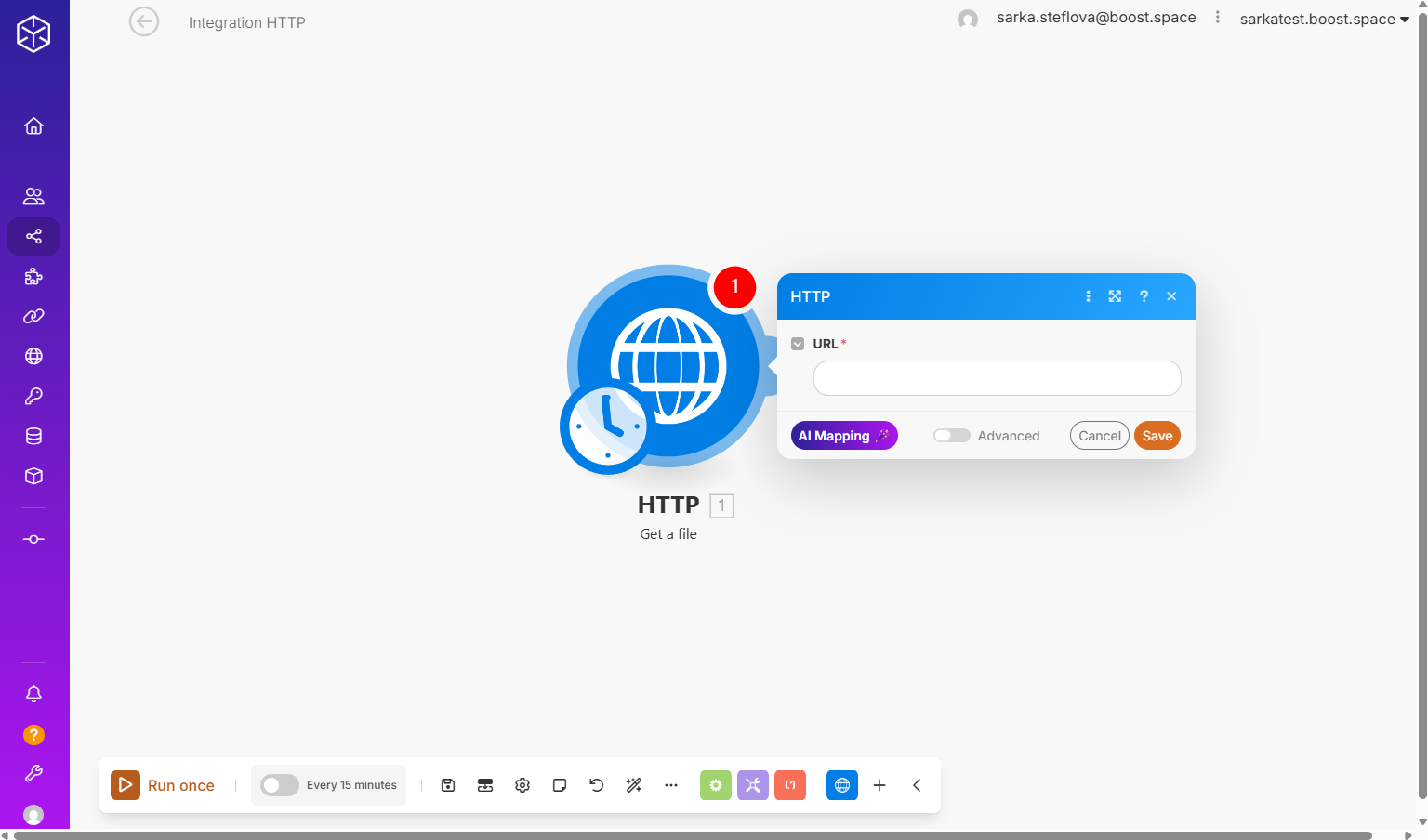
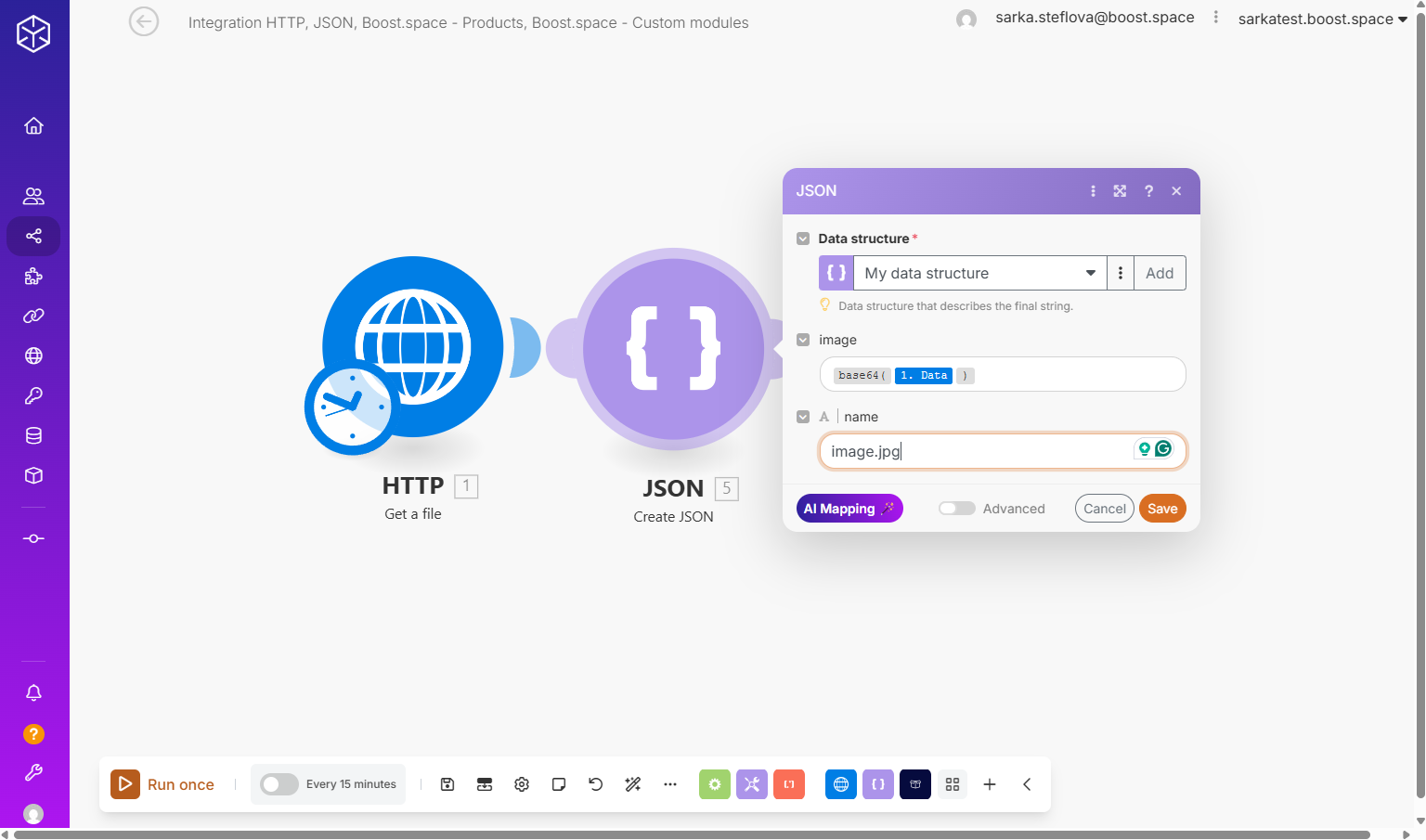
Next, the file or image is converted into a JSON data structureWhen you create a data store, you need to create a data structure that formats your data store in Boost.space Integrator. Think of the data store as a spreadsheet and the data structure as the headers. The data structure defines the kind of data (i.e. text, numeric, etc.) that the data store records. You can view and manage your data... that contains:
- image (or file) – it depends on what you map into a data structure. The file’s content, encoded in
base64format to ensure correct transfer and storage - name – the file’s designated name, such as
image.jpg. Or how you want, but don’t forget to add .jpg.
 Finally, the prepared data is sent to Boost.space by making an API call to the relevant module, such as Products or in this case a Custom module. This stage involves establishing a secure connectionUnique, active service acces point to a network. There are different types of connections (API key, Oauth…). using an API key, mappingMapping links the modules in your scenario. When you map an item, you connected the data retrieved by one module to another module to perform the desired action. For example, you can map the email address and subject lines from the Email > Watch emails module to Google Sheets > Add a row and create a spreadsheet of email addresses... the file to the correct custom fieldA feature in Boost.space that allows administrators to define and manage additional data fields within each module, tailoring the system to specific organizational needs., and ensuring it is stored in the intended record.
Finally, the prepared data is sent to Boost.space by making an API call to the relevant module, such as Products or in this case a Custom module. This stage involves establishing a secure connectionUnique, active service acces point to a network. There are different types of connections (API key, Oauth…). using an API key, mappingMapping links the modules in your scenario. When you map an item, you connected the data retrieved by one module to another module to perform the desired action. For example, you can map the email address and subject lines from the Email > Watch emails module to Google Sheets > Add a row and create a spreadsheet of email addresses... the file to the correct custom fieldA feature in Boost.space that allows administrators to define and manage additional data fields within each module, tailoring the system to specific organizational needs., and ensuring it is stored in the intended record.
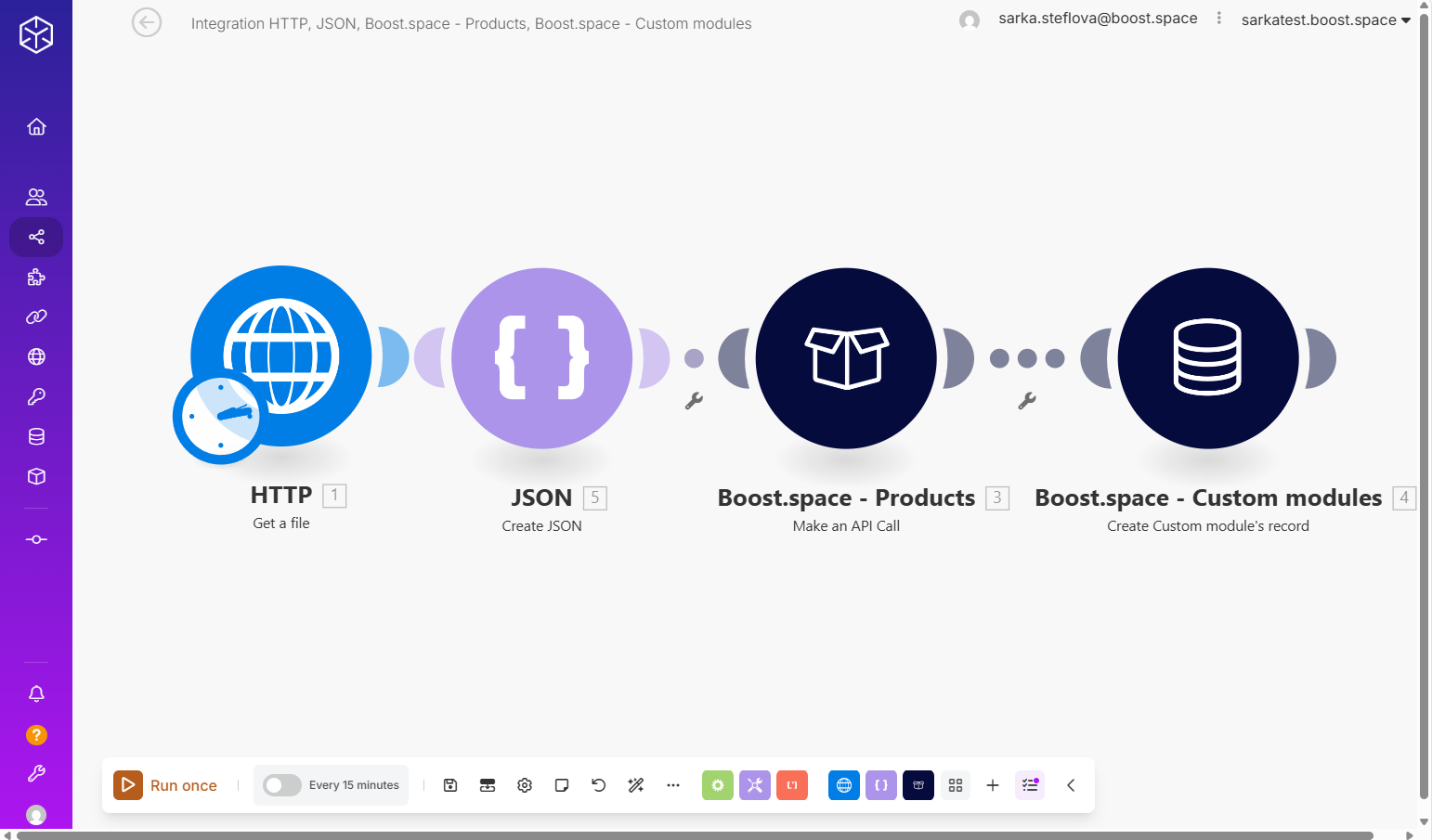
By following this method, usersCan use the system on a limited basis based on the rights assigned by the admin. can reliably and consistently upload files from any source into Boost.space, eliminating unnecessary trial and errorService is unavailable due to a failure, a service responds with unexpected data or the validation of input data fails. and ensuring smooth integration within their workflows.